2.4.2. Request for Proposals
A Request for Proposals (RFP) is a formal solicitation method that seeks to leverage the creativity and knowledge of business organizations in order to provide a solution to a unique procurement. Unlike the RFQ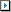 process in which the state prescribes both the specifications and solution to its own needs and suppliers replicate the state’s specifications and solutions in the bids the suppliers submit, the RFP
process in which the state prescribes both the specifications and solution to its own needs and suppliers replicate the state’s specifications and solutions in the bids the suppliers submit, the RFP process allows suppliers to propose their own comprehensive and innovative solution to the state’s needs described in the RFP
process allows suppliers to propose their own comprehensive and innovative solution to the state’s needs described in the RFP . The RFP
. The RFP seeks to identify the "best value" for the state by using a combination of technical and cost factors to evaluate suppliers’ proposals.
seeks to identify the "best value" for the state by using a combination of technical and cost factors to evaluate suppliers’ proposals.
The state entity should use an RFP if the end user wishes to evaluate the experience of the supplier and the quality of the supplier response to either a clear and accurate statement of work or to identify a supplier who can offer the best possible solution to the state entity’s identified needs. Additionally, an RFP
if the end user wishes to evaluate the experience of the supplier and the quality of the supplier response to either a clear and accurate statement of work or to identify a supplier who can offer the best possible solution to the state entity’s identified needs. Additionally, an RFP should be used when the potential for amendments or refinement of scope may be required. The RFP
should be used when the potential for amendments or refinement of scope may be required. The RFP process may only be used as a method of solicitation after a written determination has been made that the use of competitive sealed bidding (i.e., the RFQ
process may only be used as a method of solicitation after a written determination has been made that the use of competitive sealed bidding (i.e., the RFQ process) will not be practicable or advantageous to the state entity.
process) will not be practicable or advantageous to the state entity.
Unless SPD has granted delegated purchasing authority to the state entity to make the RFP
has granted delegated purchasing authority to the state entity to make the RFP certification on its own, or to use the Fast Track RFP Process, as detailed in Section 2.4.2.1., the state entity must submit a written request and justification to SPD
certification on its own, or to use the Fast Track RFP Process, as detailed in Section 2.4.2.1., the state entity must submit a written request and justification to SPD for permission to issue and conduct the RFP
for permission to issue and conduct the RFP . The following stages in this GPM
. The following stages in this GPM define the steps for conducting an RFP
define the steps for conducting an RFP , beginning with Chapter 3 - Stage 3 - Solicitation Preparation, which identifies the resources and tools SPD
, beginning with Chapter 3 - Stage 3 - Solicitation Preparation, which identifies the resources and tools SPD has provided to assist in conducting RFP
has provided to assist in conducting RFP s.
s.